- 604-423-3737
- 488 Gamma Ave Burnaby, BC V5C 0J7 Canada
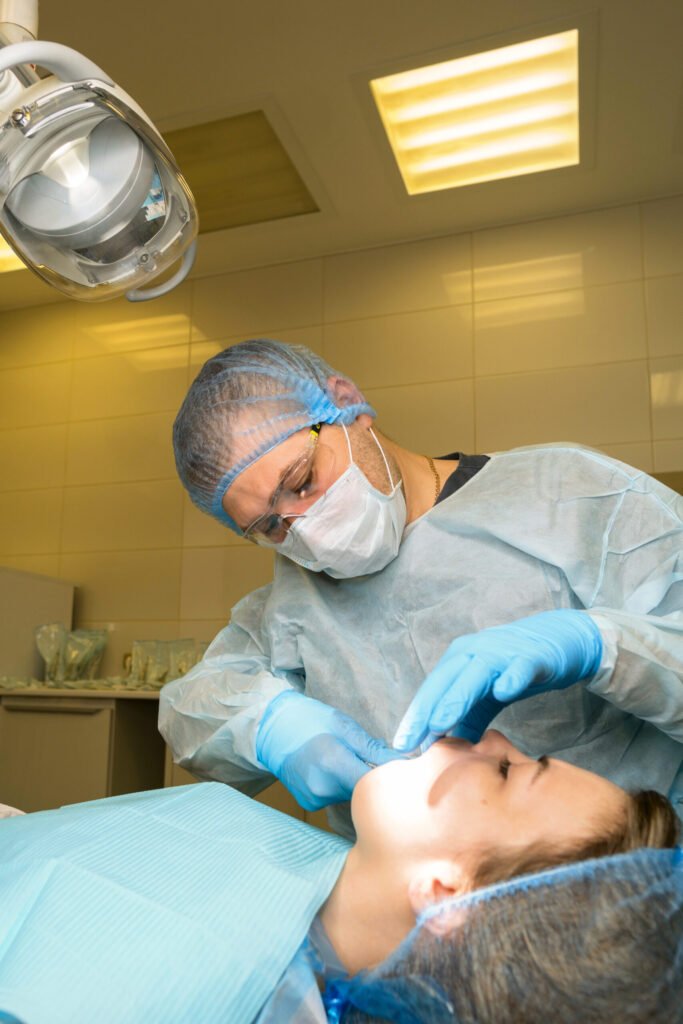
Wisdom Teeth Extraction
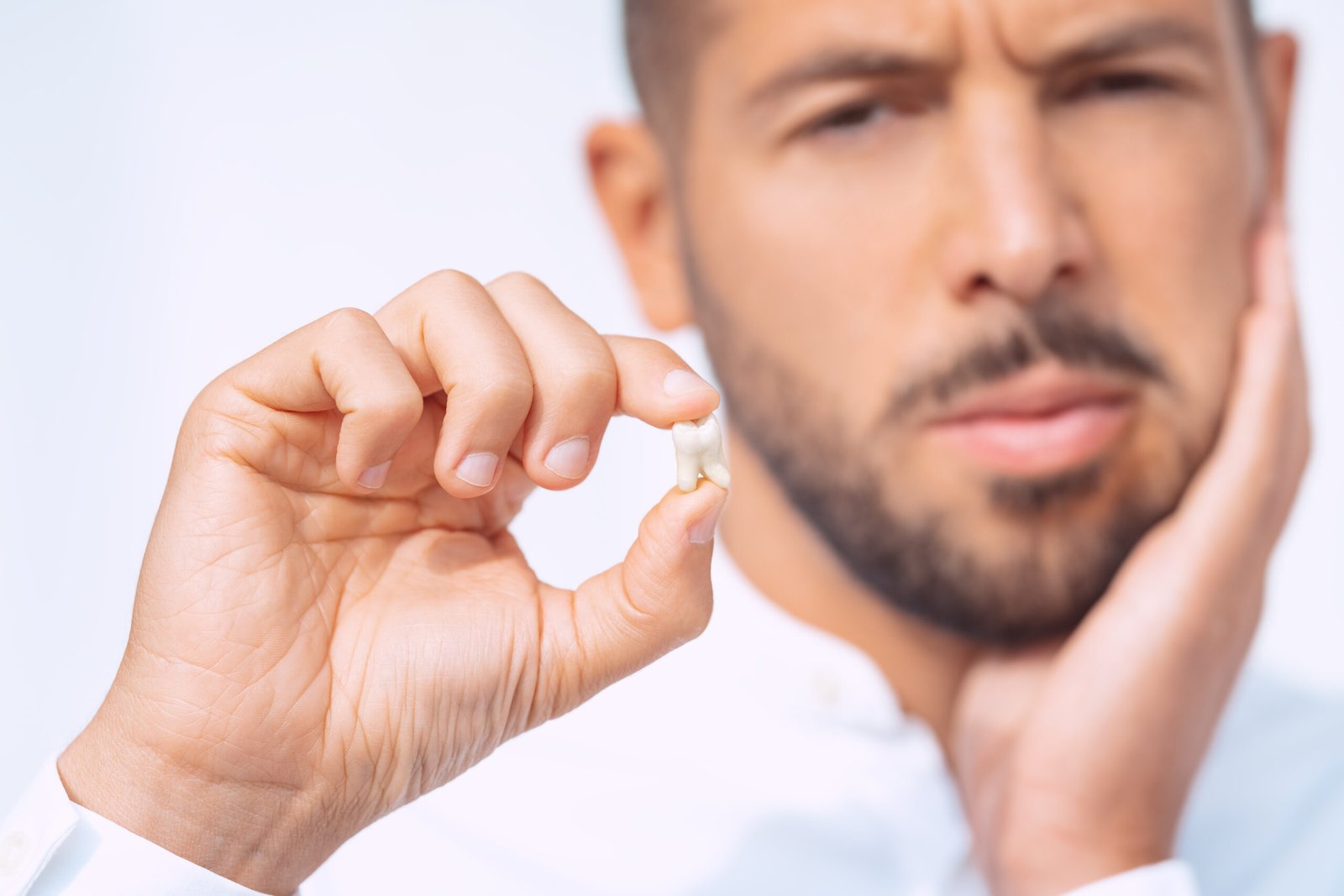
If you’re between the ages of 16-25 years, a discussion about your wisdom teeth should take place. Wisdom teeth, a third set of molars, appear in the very back of each area of your mouth: Upper left, lower left, upper right, and lower right. In a few patients, enough space exists for these molars to move into place. But most commonly, they just don’t belong, or they’re not lined up correctly. Wisdom teeth can lay entirely on their sides or lean at various angles into the neighboring teeth.

Let’s get to know each other
Wisdom teeth causing pain and infection give a clear warning sign that treatment needs consideration. But some problems can also slowly develop without your awareness. If you’re an adult with wisdom teeth, be sure they’re evaluated periodically for changes using a panoramic x-ray.
If you need to consider wisdom teeth removal, qualified dentists can discuss options with you.Various forms of sedation offer anxiety-reduction that puts this minor surgical procedure within reach of every patient that needs
Wisdom Teeth Evaluation & Extraction
The following early steps can help guard your child against tooth decay, even before their first dental visit:
Wisdom teeth can cause discomfort—or develop hidden problems without symptoms. Pain is often a sign that something needs attention, but even silent issues can lead to future complications. That’s why we recommend regular panoramic x-rays to monitor wisdom teeth. If removal is needed, we’ll ensure the process is smooth, safe, and as comfortable as possible.
- Erupted: This simply means the tooth moved through the surface of the gums just like your other teeth. Eruption generally doesn’t occur before age 16, but can happen at nearly any age after that. It may have adequate space for its position.
- Soft Tissue Impaction/Partially Erupted: The top of the tooth has emerged from the bone although excessive gum tissue usually covers it. Food trapped in the gum flap can lead to decay and infection.
- Partial Bony Impaction – The majority of the tooth sits below the jawbone level, although it’s beginning to emerge. A large flap of gum lies over this tooth and leaves it prone to infection and decay as mouth bacteria slip into the area.
- Complete Bony Impaction – In this case, the tooth has not broken the surface and remains entirely encased in the bone. While the risk of infection is low, a small percentage of these will form a cyst in the jaw. This hollow space can expand and result in fracture of the jaw.

Contact Us
- 488 Gamma Ave Burnaby, BC V5C 0J7 Canada
- 604-423-3737
- info@simplywellnessdental.ca
-
Monday to Thursday : 7:15am – 7:00pm
Friday to Sunday – 9:00am – 5:00pm
Follow US
REQUEST AN
APPOINTMENT
We’d love to help you Smile with Confidence. Call our dental office today or request an appointment online to set up your first visit. We’ll be in touch soon.
